Trouma
1. Broken Bone / Fracture
In simple words when the bone breaks either complete or incomplete, it is called fracture. It can happen at any age from child to old age person. It is very common across the world. With proper treatment you will be back to your normal life.
- Closed or open fractures:depending on the overlying skin condition if the skin is intact and bone is not exposed, it is called close fracture. The other way if bone is exposed through the skin, it is called open fracture. Commonly open fracture has more complication.
- Complete or incomplete fracture:Depending on the break whether it progress across the full width of the bone or not.
- Displaced or displaced fracture:Depending on the alignment of the bone fragment after fracture. If the fracture is displaced it requires surgery for the good healing.
- Avulsion:if the attached ligament or tendon come off the bone with chip of bone it is called avulsion fracture.
- Comminuted: bone breaks in the multiple pieces.
- Pattern of fracture line –Oblique, spiral, transverse
- Epiphyseal injury
- Strong force like in fall from height, vehicle accident and sports injury – common in young people
- Low force like simple fall at home from stairs or in bathroom- common in old age people and in weak bones (osteoporosis)
- Repeated activity or over usage may lead to the fracture – called stress fracture
Depending upon the type of injury and fracture, symptoms may be mild or severe.
- Severe pain
- Swelling
- Bruising
- Difficulty in using injured limb
- Visible bent or deformity at the injury site
- Numbness over the involved limb
- X-rays: most common used test that shows the break in the bone, type of the fracture and helps in the treatment plan. easily available and reliable test for fracture diagnosis
- CT scan: it provides detail analysis of the fracture like direction of fractures, number of bone pieces, type of fracture displacement. We can also made 3D images of fracture for better analysis and treatment planning.it is most commonly used in complex fractures involving joint surface.
- MRI: it provides good details of soft tissue like tendon, ligament and muscle. So whenever treating doctor suspect soft tissue injury along with the bone MRI is useful.
- Slab – support the limb from one side only.it immobilize the fracture and helps in bone healing in place.it can be made by plaster of Paris or fibre.
- Cast- support the limb from all side. It is more stable compared to slab.
- Traction- it requires some pulley a weight to stretch the muscle and tendon around the fracture to realign the fracture.
- Splint- they are ready made and can be easily used for immobilization of the fracture of certain type. They are available in various sizes and can be easily wear and removed by patient themselves.
- Surgery- if fracture is displaced, involves the large bones, complex injury, open fracture or comminuted then it may require surgery.
Surgery can be open reduction and fixation with plate and screws, rod or nail insertion in the bone, replacement of the fracture part or simple screw placement.
- Healing process depend on the various factors
- Age of the patient
- Site of the fracture
- Type of fracture
- Severity of injury
- Associated injury
- Type of treatment
- Nutritional status of the patient
- Habits like smoking, alcohol
Usually healing of the bone takes around 6-12 weeks. Sometimes it may take less or more time than usual.
- Pain after surgery is expected from natural healing process and inflammation.
Doctor will give combination of medication to control the pain
- Weight Bearing- for leg fractures-patient needs crutches or a walker for a period of time
partial weight bearing -after 6 to 8 weeks.
Full weight bearing – after fracture union usually take 3 – 4 months.
It is important to follow doctor’s advice strictly to prevent complication.
- Physical Therapy
After surgery, physiotherapy will teach how to use crutches /walker
Basic physiotherapy according to your fracture type and surgery to prevent the stiffness and make you mobile early.
Follow the physiotherapy instruction to regain pain free full movement and built your strength to perform daily activity.
- Sports and Fitness Activities
After 6 -12 months doctor may allow you to do low impact level activity like swimming and cycling depending on your fracture and healing.
- There is certain common complication like infection, joint stiffness, blood clots, arthritis, avascular necrosis, compartment syndrome, delayed healing malunion, non-union or nerve /vessel injury.
- Fracture is an emergency situation; you should try to contact orthopaedic doctor as soon as possible to prevent complication.
- If you feel that swelling or pain is not bearable or fracture is taking long time for healing or if you find any infection at the fracture area then you should contact the doctor. you should immediately call the doctor.
2. Lower extremity fractures
Pelvis and acetabulam fracture
- This type of fractures are common in high energy trauma like vehicular accident or fall from height and more often then associated with head,chest,abdomen and spine injuries.
- Thses injuries are serious in nature and require hospital admission.
- Treatment can be conservative with traction and rest or operative with plate and screw fixation depending on the fracture type.
- Recovery will take around 3-4 months and depends on the severity of fracture and associated injury.
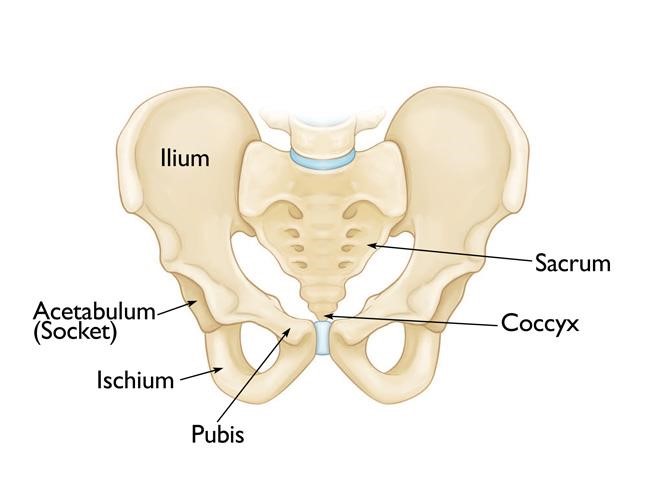
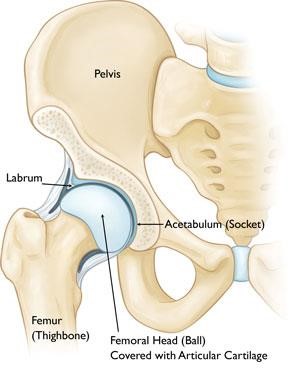
Hip dislocation
- Ball(femur head) of the hip joint moves out of its socket(acetabulam) in hip dislocationThis type of fractures are common in high energy trauma like vehicular accident or fall from height. Most commonly hip dislocate in posterior direction but can be anterior , inferior or central.
- Thses injuries are serious in nature and require urgent hospital admission.
- Treatment involves reduction under seadation followed by traction and rest for 3 -4 weeks
- As it involves the joint there is risk of developing avascular necrosis of hip joint , arthritis and stiffness in the future.
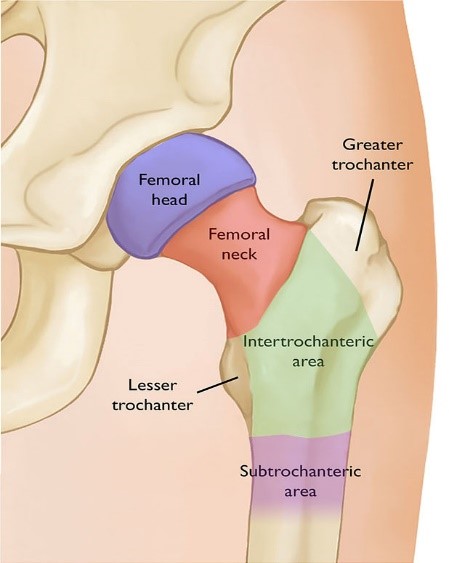
Fracture around the hip joint – neck femur fracture , intertrochanteric fracture or subtrochanteric fracture
- Most common fracture in the old age group patient. These occurs dut to simple fall at home, accidents or fall from height. Patient requires hospital admission and traction for the pain relief.
- Most of the fracture require surgical treatment like screw, plate and screw,rod with screw ot replacement of the hip joint(hemi/total replacement).
- Recovery take place in 4-6 months depending on the fracture type and surgery.
Thigh (femur)/leg(tibia – fibula)/ long bone fracture
- thigh and leg bone are one of he strongest bone in the body. It require high energy to break the bone most commonly seen in the young patient and in vehicular accident.
- There is considerable amount of blood loss and othe injury associated with these fractures.
- Treatment require urgent hospital admission and traction or splint for immbilization. Fracture routinely fixed with rod and screws but sometimes if associated injury or skin condition is not good may require external fixation.
- Recovery will take place in 6-8 mnths duration.
Fracture around the knee joint- distal femur, patella, upper tibia
- These injuries are quite common as knee joint has less muscular prtection in front.
- It can occur with vehicular accident, fall or sports. It is aasociated with ligament injury in the knee.
- Simple patella and tibia fracture can be treated with splint and rest while diplaced fracture reuire fixation with wire,plate and screws.
- As the fractures involves the joint post trauma stiffness and arthritis can occur.

Fracture around ankle joint- distal tibia, malleolus, talus and calcaneum fractures
- These fractures can occur after twisting injury, fall from height, vehicular accident and sports. Ankle ligament sprain are one of the commonest injuries.
- Simple, undisplaced fractures can be treated with below knee splint and rest – 6-8 weeks. Displaced and fracture involving joint surface require operative fixation with plate and screws, wire or rods. Post traumatic arthritis and stiffness can occur.
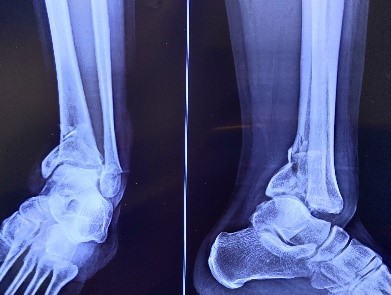
Fracture in the foot
- Metatarsal fractures are common after simple fall and foot twisting injury.
- Majority of the fractures are treated with below knee splint and rest for 4-6 weeks . some displaced fractures may require wire or plate fixation .
- recovery occurs within 6-8 weeks without major complication.
- Dancer fracture – it is avuslin fracture of the last metatarsal bone commonly seen in the dancer and forcefull foot twisting injury. Undisplcard fracture treated with below knee splint and rest for 4-6 weeks. For displcad fracture wire ot screw fixation may be required.

Lisfranc injury
this is a midfoot injury involving base of 2 nd metatarsal and supporting ligaments. This injury is commonly missed in simple x ray so it may require special view.
Most of the fractures are unstable in nature, so they require operative fixation with wire, screws and plates. without proper treatment patient may develop midfoot pain and arthritis.
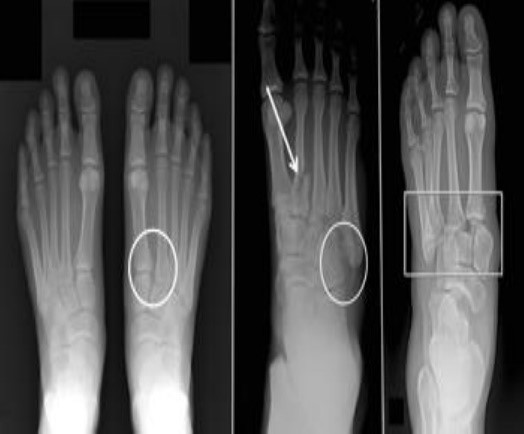
Jones fracture
- fracture of the last metatarsal at the junction of shaft and base. Common after twisting injury of foot or fall.
- This fracture has tendency of not healing due to low blood supply. So, patient has to take strict rest for fracture healing with splint.
- If fracture not unite in 8-12 weeks, then screw fixation is required.
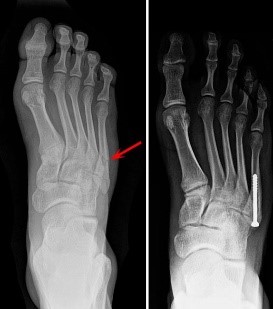
3. Upper extremity fractures
Fracture around shoulder – clavicle, proximal humerus (upper end of humerus), scapula (blade of shoulder joint)
- Most common fracture in the young as well in old age These occurs dut to simple fall at home, accidents or fall on outstreched hand.
- Clavicle , scapular blade and simple proximal humerus fractures can be treated with immobilization for 3 weeks and rest.
- Most of the displaced fracture require surgical treatment like screw, plate and screw, rod with screw. Very comminuted proximal humerus fractures may require replacement of the shoulder joint (hemi/ reverseshoulder replacement).
- Recovery take place in 4-6 months depending on the fracture type and surgery.
Shoulder dislocation
- Ball(humeral head) of the shoulder joint moves out of its socket(glenoid) in shoulder This type of injury are common in high energy trauma like vehicular accident, fall or siezures . Most commonly hip dislocate in anterior direction but can be posterior , inferior. It may be associated with fracture of greater tuberosity.
- Thses injuries are serious in nature and require urgent hospital admission.
- Treatment involves reduction under seadation followed by shoulder arm sling for 2 weeks and rest.
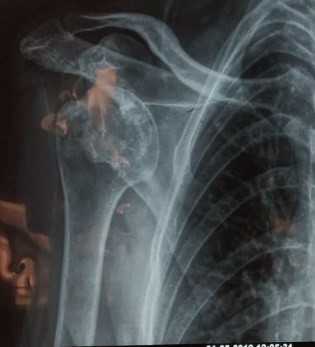
Elbow dislocation
- Olecrenon process (hook) of the elbow joint moves out of its socket(olecernon fossa) in elbow This type of injury are common in high energy trauma like vehicular accident, fall on outstreched hand . Most commonly elbow dislocate in posterior direction but can be medial or lateral. It may be associated with fracture of olecrenon or radial head.
- Thses injuries are serious in nature and require urgent hospital admission.
- Treatment involves reduction under seadation followed by above elbow splint for 2 weeks and rest.
Fractures of arm (humerus shaft) / forearm (radius – ulna)
Humerus fracture with plate fixation
- arm and forearm bones are comparatively strong bone in the body. It require high energy to break the bone most commonly seen in the young patient with vehicular accident or fall from height.
- Treatment require urgent hospital admission and splint for immbilization. Fracture routinely fixed with rod and plate-screws but sometimes if associated injury or skin condition is not good may require external fixation.
- Excessive swelling in the forarm can lead to compartment syndrome which leads to damage to muscle and nerves. so it require coninuous observation by doctor.
- Recovery will take place in 3-4 mnths duration.
Fracture around wrist joint– distal radius, scaphoid
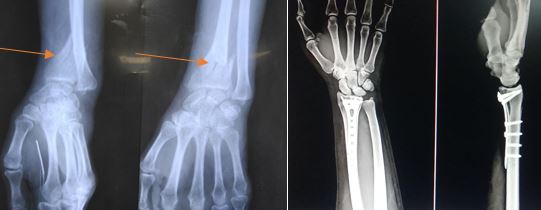
- Distal radius fracture is one of the most common fracture in the body. Simple fall on out stretched hand, vehicular accident or sports injury can lead to this fracture. Common in old age patient due to osteoporosis.
- Minimal displaced fractures can be treated with below elbow cast for 4-6 weeks. Displaced fracture require fixation with wire or plate and screws.
- As the fracture involves the articular surface post traumatic arthritis and stiffness may occur.
- Scaphoid fractures common in young patient. As scaphoid has less blood supply some fractures may not heal and require surgical fixation and bone grafting for non-union.
Fracture in hand– metacarpal and phalanx fracture
Metacarpal fractures
- common after simple fall or direct blow over hand.
- Majority of the fractures are treated with below elbow splint and rest for 4-6 weeks . some displaced fractures may require wire or plate fixation .
- recovery occurs within 6-8 weeks without major complication.
Finger fracture
- common after simple fall, twisting or direct blow over toes.
- Treatment involves simple buddy strapping for 3 weeks. Sometime for displaced fracture or open fracture wire fixation required.
Bennet and Rolando fracture
fracture of the base of the 1 st metacarpal(thumb) involving the joint Surgery required for fixation with wire or plate – screws.
Boxer fracture
fracture of last metacarpal neck portion with displacement. Common after punching injury. For displaced fracture wire fixation is required.
Caplan dislocation- palmer dislocation of the 2 nd metacarpophalangeal joint (index finger) is called caplan dislocation. This injury is difficult to treat just by simple traction. Open surgery required for the reduction of the dislocation followed by splint for 3-4 week
4. Pediatric fracture
Epiphyseal or growth plate injury
- Epiphyseal or growth plate present in the of long bone of children and adolescent. It helps the growth of the bone in length.
- This injury is common in children due to fall and most commonly involve the bone near wrist, knee, ankle, elbow and shoulder joint.
- The diagnosis requires careful examination of the x ray and sometime may require MRI for the confirmation.
- This injury is classified according to salter Harris classification depending on the fracture pattern in type 1 to 6. Type 1 and 2 are the common type of injury and can be managed with close reduction and cast. Type 3 to 6 injury are severe in nature and may require surgery and wire or plate fixation.
- The common complications are growth disturbance, deformity or bony spur formation.
Common fractures in children
Long bone fractures- femur /tibia/humerus/radius /ulna
- Complete fracture- common in arm(humerus), forearm (radius – ulna), thigh(femur) and leg bones (tibia – fibula) and collar bone(clavicle). common after fall or twisting injury. Fracture can be simple displaced, spiral, oblique or transverse in nature. Most of the fractures can be treated with simple immobilization with cast and rest for 2-4 weeks. Severe displaced fracture may require surgery with wire or rods. As healing potential of the bone is good, fracture unite soon.
- Green stick fracture- common in forearm bone (radius and ulna) after fall and bending force. Bone in the children have thick covering called periosteum. So, you can see only bending of the bone without complete fracture on the x ray. Treatment requires to reduce the fracture and straight under sedation and apply cast for 3-4 weeks.
- Torus fracture/buckle fracture- It is an incomplete fracture of the long bones due to loading along the length. common in wrist and ankle region. You can see bulging in the cortex on x ray. Treatment requires immobilization in splint for 3-4 weeks.
Supracondylar humerus fractures
- Most common fracture in children in which bone just above the elbow joint break due to fall on outstretched hand. Fracture is associated with open injury, injury to nearby blood vessel and nerves. So urgent and careful evaluation is required by the doctor.
- Simple displaced fracture treated with above elbow cast for 3 – 4 weeks. Displaced fracture requires urgent reduction under sedation and fixation with wire followed by splint for 3-4 weeks. If fracture is not reduced properly it can lead to malunion and deformity formation at the elbow joint.
5. Open fracture
- When the bone is exposed at the fracture to outside due to break in the skin and surrounding soft tissue, it is called open fracture.
- It is common after vehicular accident or fall from height. Most commonly seen in leg, thigh and forearm fractures. Open fracture is classified according to size of wound, severity of bone and soft tissue injury and vessel or nerve injury.
- Complication like infection, delayed fracture healing, nonunion and compartment syndromes.
Treatment
- debridement – removal of dead tissue, foreign body and dirt followed by thorough wash with antiseptic and normal saline (6-9 liter)
- external fixation – stabilization of the fracture by inserting metal pins through skin in the bone above and below fracture and fixed outside the skin to the metal frame. It can be temporary fixation or final fixation depending on the fracture pattern
- illizarov fixation- type of external fixator using rings outside skin for complex open injury
- antibiotic treatment- broad spectrum coverage provided with 2 or 3 antibiotics to prevent infection
- dressing – simple or negative pressure dressing (VAC) done according to type of wound.
6. Minimal invasive surgery
Fracture fixation like plate and rod with screws can be performed through small skin incision using special instruments for less pain, shorter stay and fast recovery. Special surgical tools used in minimal invasive surgery
Advantages of Minimal invasive surgery
- Shorter hospital stays
- Less pain after surgery
- Quick recovery and return to activities of daily living
- Can be done under local anaesthesia
- Reduced risk of infection
- Less blood loss during surgery
- Less damage to soft tissue
- Small scar
- Better postoperative quality of life
